Saved Views
Saved Views in Telescope make it easy to preserve and reuse custom configurations of the Explorer. Instead of manually setting filters or fields every time, you can save them as named presets and switch between them like bookmarks. Unlike browser bookmarks, Saved Views support full-text search, sharing, and better integration with the system.
Purpose
Section titled “Purpose”Saved Views simplify repetitive workflows by allowing users to:
- Quickly switch between different perspectives of log data
- Share useful views with teammates
- Avoid storing raw URLs in external tools or bookmarks
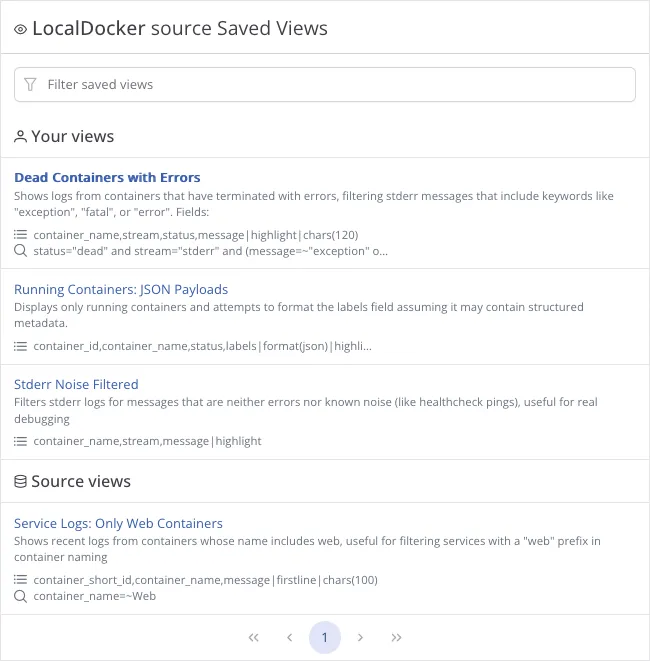
Always Bound to a Source
Section titled “Always Bound to a Source”Every Saved View is always associated with a specific Source. There are no standalone views. When no view is explicitly selected, Telescope uses a default view, which reflects the default configuration of the current source.
View Scopes
Section titled “View Scopes”There are two types of Saved Views:
Personal Views
Section titled “Personal Views”- Created by a user for a specific source
- Only visible by the creator by default
- Can be marked as
shared, which allows any user with access to the source to use (but not edit) it - If a user loses access to the source, all related views become inaccessible
- Only the creator can edit or delete their personal views
- Can be changed to source scope at any time if the user has permission to edit the source
Source Views
Section titled “Source Views”- Exist at the source level and are available to any user who has access to the source
- Editable by users with source-edit permissions
View List Ordering & Search
Section titled “View List Ordering & Search”When displaying saved views:
- Personal views of the current user
- Source-level views
- Shared views created by others
Telescope uses full-text search across view name, description, filters, fields, and other saved parameters.
Limits
Section titled “Limits”Administrators can control the number of views a user can create via the configuration file.
By default, the limit is 0, meaning no restriction.
limits: max_saved_views_per_user: 0Activation and Execution
Section titled “Activation and Execution”When a Saved View is selected:
- All stored parameters are applied to the Explorer
- The data is not immediately fetched - you must press Execute to run the query and see the results
Creating a View
Section titled “Creating a View”To create a view:
- Open the “Views” menu and select “Save new view as…”
- Provide a name, scope (
personal/source), and optional description - A URL-friendly
slugis automatically generated from the name (slug regeneration may be added later)
This slug is used in the URL, so it clearly reflects the view’s purpose.
Actions in the Views Menu
Section titled “Actions in the Views Menu”Depending on permissions and state:
- Save new view as… – Create a new view from the current state
- Reset to default view – Revert to the system default view
- Save – Overwrite the current view with updated fields, filters, etc. (name and description stay unchanged)
- Edit view – Modify name, description, scope, or sharing options
- Delete – Remove the view (if the user has permission)
URL Behavior
Section titled “URL Behavior”After selecting a view and running Execute:
- The URL includes only the
viewparameter (e.g.?view=errors-by-service-4b7fc23) - If the user modifies filters or fields, the URL is updated accordingly
- Partial overrides are supported-— e.g. a view may define filters and fields, but you can adjust them without breaking the base view reference
Stored Parameters
Section titled “Stored Parameters”A Saved View currently stores:
- Fields data
- FlyQL query
- Raw SQL
WHEREquery (if used) - Time range (
from/to) - Graph settings (visibility, group by field)
- Limit
- Context fields (e.g. container names for Docker sources)
Future Work
Section titled “Future Work”- A dedicated management page for personal views
- Slug regeneration by request
- Usage statistics for view